HDFS Transparent Encryption
Data encryption is now mandatory for several different government, financial, and regulatory entities across the world. The healthcare industry has HIPAA regulations, the card payment industry has PCI DSS regulations, and the United States government has FISMA regulations. Encrypting data in HDFS will allow your organization to comply with such regulations. HDFS transparent encryption implements transparent, end-to-end encryption of HDFS data, without requiring any changes to user application code. While encryption performed at the application level can be more flexible, the procedure to configure each application individually to support encryption is difficult and prone to errors. Integrating encryption directly into HDFS allows existing applications to operate on encrypted data without any code changes.
The salient features of HDFS encryption are:
- Only HDFS clients can encrypt or decrypt data. The encryption is end-to-end, thus securing data at-rest, and in-transit.
- Key management is not integrated with HDFS. HDFS does not have access to unencrypted data or encryption keys. Hence, the key administrator does not need to be an HDFS administrator. This allows for a separation of duties so that nobody has unrestricted access to the data and keys.
- The operating system and HDFS only interact using encrypted HDFS data. This provides a level of security against OS-level and file-system-level attacks.
- Currently, AES-CTR is the only supported encryption algorithm. AES-CTR uses either a 128- or a 256-bit encryption key (when an unlimited strength JCE is installed). A very important optimization was making use of hardware acceleration in OpenSSL 1.0.1e using the AES-NI instruction set, which can be an order of magnitude faster than software implementations of AES.
- Enabling HDFS encryption should not lead to a loss in performance. To ensure HDFS continues to perform at optimal levels, use the AES-NI instruction set to accelerate the encryption process. For instructions, see Optimizing Performance for HDFS Transparent Encryption.
Key Concepts and Architecture
Keystores and the Hadoop Key Management Server
Integrating HDFS with an external, enterprise-level keystore is the first step to deploying transparent encryption. This is because separation of duties between a key administrator and an HDFS administrator is a very important aspect of this feature. However, most keystores are not designed for the encrypt/decrypt request rates seen by Hadoop workloads. This led to the development of a new service, called the Hadoop Key Management Server (KMS), which serves as a proxy between HDFS clients and the backing keystore. Both the keystore and Hadoop KMS must use Hadoop’s KeyProvider API to interact with each other and with HDFS clients.
While HDFS encryption can be used with a local Java KeyStore for key management, Cloudera does not recommend this for production environments where a more robust and secure key management solution should be used. Cloudera Navigator Key Trustee Server is a key store for managing encryption keys and other secure deposits. To integrate with the Navigator Key Trustee Server, Cloudera provides a custom KMS service, called the Key Trustee KMS.
The diagram below illustrates how HDFS clients and the NameNode interact with an enterprise keystore, in this case, Navigator Key Trustee, through the Hadoop Key Management Server.
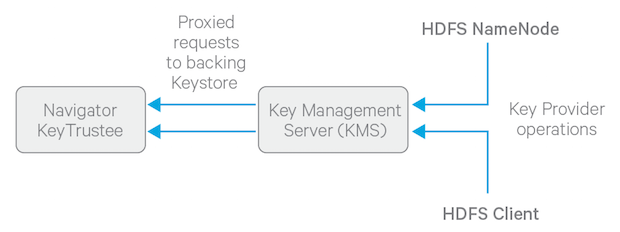
To get started with deploying the KMS and a keystore, see Enabling HDFS Encryption Using the Wizard.
For information on configuring and securing the KMS, see Configuring the Key Management Server (KMS) and Securing the Key Management Server (KMS).
Encryption Zones and Keys
HDFS transparent encryption introduces the concept of an encryption zone (EZ), which is a directory in HDFS whose contents will be automatically encrypted on write and decrypted on read. Encryption zones always start off as empty directories, and tools such as distcp can be used to add data to a zone. Every file and subdirectory copied to an encryption zone will be encrypted. You cannot rename files or directories once they have been added to a zone.
 Note: An encryption zone cannot be created on top of an existing directory.
Note: An encryption zone cannot be created on top of an existing directory.Each encryption zone is associated with a key (EZ Key) specified by the key administrator when the zone is created. EZ keys are stored on a backing keystore external to HDFS. Each file within an encryption zone has its own encryption key, called the Data Encryption Key (DEK). These DEKs are encrypted with their respective encryption zone's EZ key, to form an Encrypted Data Encryption Key (EDEK).
The following diagram illustrates how encryption zone keys (EZ keys), data encryption keys (DEKs), and encrypted data encryption keys (EDEKs) are used to encrypt and decrypt files.
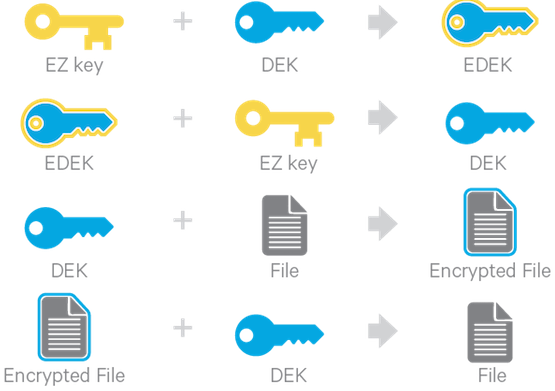
EDEKs are stored persistently on the NameNode as part of each file's metadata, using HDFS extended attributes. EDEKs can be safely stored and handled by the NameNode because the hdfs user does not have access to the EDEK's encryption keys (EZ keys). Even if HDFS is compromised (for example, by gaining unauthorized access to a superuser account), a malicious user only gains access to the encrypted text and EDEKs. EZ keys are controlled by a separate set of permissions on the KMS and the keystore.
An EZ key can have multiple key versions, where each key version has its own distinct key material (that is, the portion of the key used during encryption and decryption). Key rotation is achieved by bumping up the version for an EZ key. Per-file key rotation is then achieved by re-encrypting the file's DEK with the new version of the EZ key to create new EDEKs. HDFS clients can identify an encryption key either by its key name, which returns the latest version of the key, or by a specific key version.
For more information on creating and managing encryption zones, see Managing Encryption Keys and Zones.
Accessing Files Within an Encryption Zone
To encrypt a new file, the HDFS client requests a new EDEK from the NameNode. The NameNode then asks the KMS to decrypt it with the encryption zone's EZ key. This decryption results in a DEK, which is used to encrypt the file.
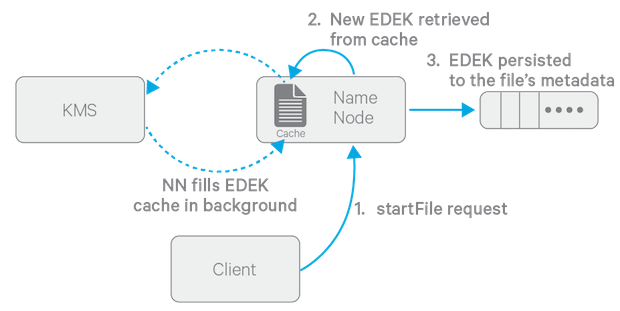
The diagram above depicts the process of writing a new encrypted file. Note that the EDEK cache on the NameNode is populated in the background. Since it is the responsibility of KMS to create EDEKs, using a cache avoids having to call the KMS for each create request. The client can request new EDEKs directly from the NameNode.
To decrypt a file, the HDFS client provides the NameNode with the file's EDEK and the version number of the EZ key that was used to generate the EDEK. The NameNode requests the KMS to decrypt the file’s EDEK with the encryption zone's EZ key, which involves checking that the requesting client has permission to access that particular version of the EZ key. Assuming decryption of the EDEK is successful, the client then uses this DEK to decrypt the file.
Encryption and decryption of EDEKs takes place entirely on the KMS. More importantly, the client requesting creation or decryption of an EDEK never handles the EZ key. Only the KMS can use EZ keys to create and decrypt EDEKs as requested. It is important to note that the KMS does not store any keys, other than temporarily in its cache. It is up to the enterprise keystore to be the authoritative storage for keys, and to ensure that keys are never lost, as a lost key is equivalent to introducing a security hole. For production use, Cloudera recommends you deploy two or more redundant enterprise key stores.
Attack Vectors
| Type of Exploit | Issue | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Access Exploit | ||
|
These exploits assume the attacker has gained physical access to hard drives from cluster machines, that is, DataNodes and NameNodes. |
Access to swap files of processes containing DEKs. This exploit does not expose cleartext, as it also requires access to encrypted block files. | It can be mitigated by disabling swap, using encrypted swap, or using mlock to prevent keys from being swapped out. |
| Access to encrypted block files. This exploit does not expose cleartext, as it also requires access to the DEKs. | It can only be mitigated by restricting physical access to the cluster machines. | |
| Root Access Exploits | ||
|
These exploits assume the attacker has gained root shell access to cluster machines running DataNodes and NameNodes. Many of these exploits cannot be addressed in HDFS, since a malicious root user has access to the in-memory state of processes holding encryption keys and cleartext. For these exploits, the only mitigation technique is carefully restricting and monitoring root shell access. |
Access to encrypted block files.
By itself, this does not expose cleartext, as it also requires access to encryption keys. |
No mitigation required. |
| Dump memory of client processes to obtain DEKs, delegation tokens, cleartext. |
No mitigation. |
|
| Recording network traffic to sniff encryption keys and encrypted data in transit.
By itself, insufficient to read cleartext without the EDEK encryption key. |
No mitigation required. | |
| Dump memory of DataNode process to obtain encrypted block data.
By itself, insufficient to read cleartext without the DEK. |
No mitigation required. | |
| Dump memory of NameNode process to obtain encrypted data encryption keys.
By itself, insufficient to read cleartext without the EDEK's encryption key and encrypted block files. |
No mitigation required. | |
| HDFS Admin Exploits | ||
|
These exploits assume that the attacker has compromised HDFS, but does not have root or hdfs user shell access. |
Access to encrypted block files.
By itself, insufficient to read cleartext without the EDEK and EDEK encryption key. |
No mitigation required. |
| Access to encryption zone and encrypted file metadata (including encrypted data encryption keys), using -fetchImage.
By itself, insufficient to read cleartext without EDEK encryption keys. |
No mitigation required. | |
| Rogue User Exploits | ||
| A rogue user can collect keys to which they have access, and use them later to decrypt encrypted data. | This can be mitigated through periodic key rolling policies. | |
| << Resource Planning for Data at Rest Encryption | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Optimizing Performance for HDFS Transparent Encryption >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |